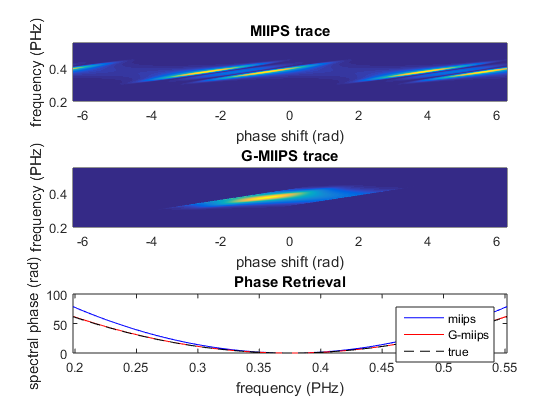
Simulation of Gmiips with 2nd order spectral phase
Contents
Set up chirped Gaussian pulse
p = gaussianPulse('f0',300/800, 'fwhm', 5, 'units', 'fs', 'dt', 0.5); GDD = 100; % fs^2 p.polynomialPhase([GDD 0 0])
Simulate Gmiips
maxGDD = 200; % fs^2 tau = p.calculateShortestDuration(); amp = maxGDD/tau^2; phasesteps = linspace(-2*pi, 2*pi, 500); % simulate standard miips m = Gmiips(p, amp, tau, phasesteps, 'gateWidth', []); % simulate Gmiips mg = Gmiips(p, amp, tau, phasesteps, 'gateWidth', 1, 'modulationFunction', 'psin');
Plot results
The dashed lines on the MIIPS maps indicate (from left to right) maximum GDD (=amp*tau^2), zero GDD, minimum GDD (= -amp*tau^2). The black solid line indicates the maxima of the SHG for each frequency.
figure(1) subplot(3,1,1) pcolor(m.phaseArray, m.frequencyArray, m.trace); shading interp ylim([-2,2]*p.bandwidth+p.centralFrequency) xlabel('phase shift (rad)') ylabel(['frequency (', p.frequencyUnits, ')']) title('MIIPS trace') subplot(3,1,2) pcolor(mg.phaseArray, mg.frequencyArray, mg.trace); shading interp ylim([-2,2]*p.bandwidth+p.centralFrequency) xlabel('phase shift (rad)') ylabel(['frequency (', p.frequencyUnits, ')']) title('G-MIIPS trace') subplot(3,1,3) plot(p.frequencyArray, m.retrievedPhase, 'b', ... p.frequencyArray, mg.retrievedPhase, 'r', ... p.frequencyArray, p.spectralPhase, 'k--'); legend('miips', 'G-miips', 'true') xlim([-2,2]*p.bandwidth+p.centralFrequency) xlabel(['frequency (', p.frequencyUnits, ')']) ylabel('spectral phase (rad)') title('Phase Retrieval')